Gang
gang plugin
Overview
The Gang scheduling strategy is one of the core scheduling algorithms of the Volcano-Scheduler. It meets the scheduling requirements of “All or nothing” in the scheduling process and avoids the waste of cluster resources caused by arbitrary scheduling of Pod. The Gang scheduler algorithm is to observe whether the scheduled number of Pods under Job meets the minimum number of runs. When the minimum number of runs of Job is satisfied, the scheduling action is executed for all Pods under Job; otherwise, it is not executed.
Scenario
The Gang scheduling algorithm based on the container group concept is well suited for scenarios that require multi-process collaboration. AI scenes often contain complex processes. Data Ingestion, Data Analysts, Data Splitting, trainers, Serving, Logging, etc., which require a group of containers to work together, are suitable for container-based Gang scheduling strategies. Multi-thread parallel computing communication scenarios under MPI computing framework are also suitable for Gang scheduling because master and slave processes need to work together. Containers under the container group are highly correlated, and there may be resource contention. The overall scheduling allocation can effectively solve the deadlock.
In the case of insufficient cluster resources, the scheduling strategy of Gang can significantly improve the utilization of cluster resources.
Binpack
Overview
The goal of the BinPack scheduling algorithm is to fill as many existing nodes as possible (try not to allocate blank nodes). In the concrete implementation, BinPack scheduling algorithm scores the nodes that can be delivered, and the higher the score, the higher the resource utilization rate of nodes. Binpack algorithm can fill up the nodes as much as possible to close the application load to some nodes, which is very conducive to the automatic expansion capacity function of K8s cluster nodes.
The BinPack algorithm is injected into the Volcano-Scheduler process as a plug-in and will be applied during the Pod stage of node selection. When calculating the Binpack algorithm, the Volcano-Scheduler considers the various resources requested by Pod and averages them according to the weights configured for each resource. The weight of each resource in the node score calculation is different, depending on the weight value configured by the administrator for each resource. Different plug-ins also need to assign different weights when calculating node scores, and the Scheduler also sets the score weights for BinPack plugins.
Scenario
The BinPack algorithm is good for small jobs that can fill as many nodes as possible. For example, the single query job in the big data scene, the order generation in the e-commerce seckill scene, the single identification job in the AI scene, and the high concurrency service scene on the Internet, etc. This scheduling algorithm can reduce the fragmentation in the node as much as possible, and reserve enough resource space on the idle machine for Pod which has applied for more resource requests, so as to maximize the utilization of idle resources under the cluster.
Priority
fair-share调度
Overview
The Priority Plugin provides the implementation of job, Task sorting, and PreempTablefn, a function that calculates sacrifice jobs. Job sorting according to priorityClassName, the task of sorting by priorityClassName, createTime, id in turn.
Scenario
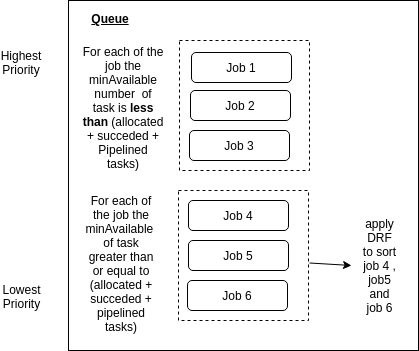
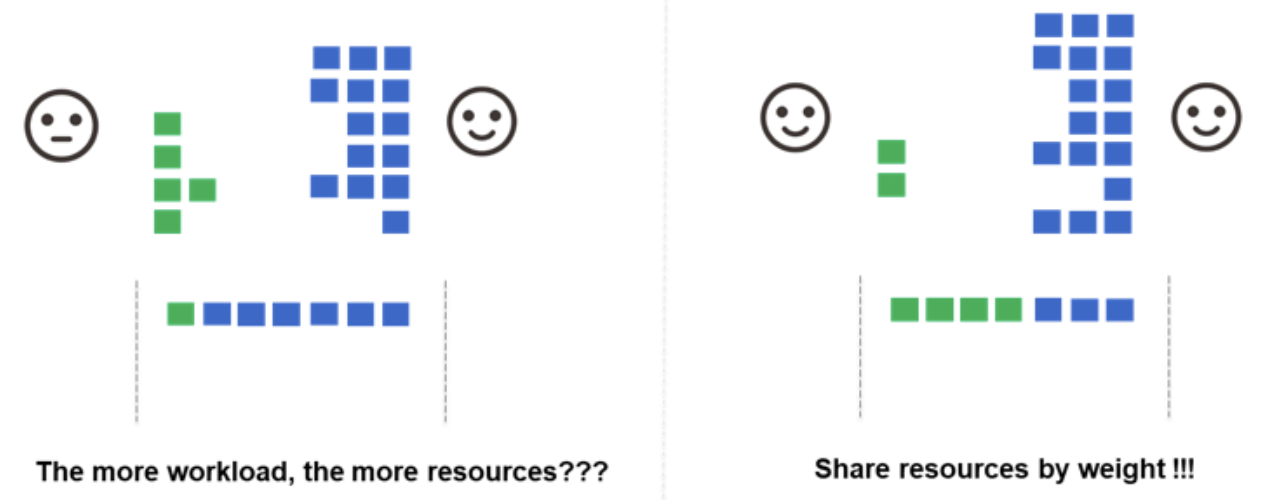
When the cluster runs multiple jobs but is low on resources, and each Job has a different number of Pods waiting to be scheduled, if you use the Kubernetes default scheduler, the Job with more Pods will eventually get more of the cluster’s resources. In this case, the Volcano-Scheduler provides algorithms that enable different jobs to share cluster resources in a fair-share.
The Priority Plugin enables users to customize their job and task priorities, and to customize scheduling policies at different levels according to their own needs. Priority is arranged according to Job’s PriorityClassName at the application level. For example, there are financial scenarios, Internet of Things monitoring scenarios and other applications requiring high real-time performance in the cluster, and the Priority Plugin can ensure that they are scheduled in Priority.
DRF
Drf plugin
Overview
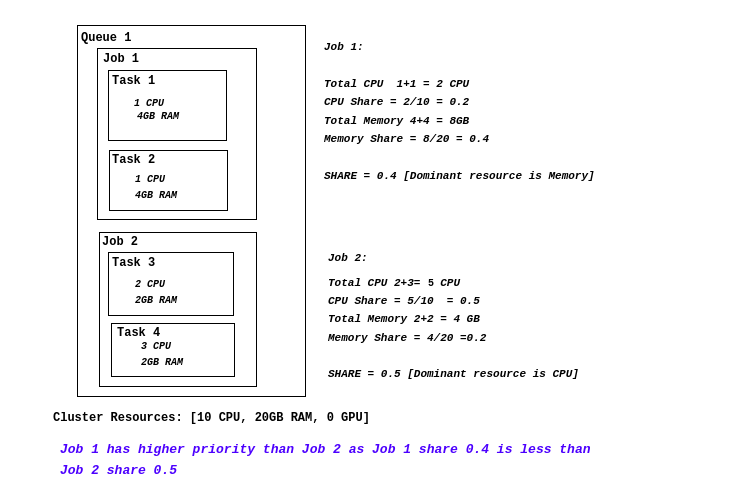
The full name of DRF scheduling algorithm is Dominant Resource Fairness, which is a scheduling algorithm based on the container group Dominant Resource. Dominant Resource is the largest percentage of all required resources for a container group. The DRF algorithm selects the Dominant Resource that is the smallest in a series of container groups for priority scheduling. This can meet more job, not because a fat business, starve a large number of small business. DRF scheduling algorithm can ensure that many types of resources coexist in the environment, as far as possible to meet the fair principle of allocation.
Scenario
The DRF scheduling algorithm gives priority to the throughput of the business in the cluster and is suitable for batch small business scenarios such as a single AI training, a single big data calculation and a query.
Proportion
Overview
Proportion scheduling algorithm uses the concept of queue to control the Proportion of total resources allocated in the cluster. Each queue allocates a certain proportion of cluster resources. For example, there are three teams that share A pool of resources on A cluster: Team A uses up to 40% of the total cluster, Team B uses up to 30%, and Team C uses up to 30%. If the amount of work delivered exceeds the team’s maximum available resources, there is a queue.
Scenario
Proportion scheduling algorithm improves the flexibility and elasticity of cluster scheduling. The most typical scenario is that when multiple development teams in a company share a cluster, this scheduling algorithm can handle the requirements of shared resource matching and isolation between different departments very well. In multi-service mixed scenarios, such as computation-intensive AI business, network IO-intensive MPI and HPC business, and storage-intensive big data business, Proportion scheduling algorithm can allocate shared resources according to demand through matching.
Task-topology
Overview
The task-topology algorithm is an algorithm that computes the priority of tasks and nodes based on the affinity and anti-affinity configuration between tasks within a Job. By configuring the affinity and anti-affinity policies between tasks within the Job and using the Task-Topology algorithm, tasks with affinity configurations can be scheduled to the same node first, and PODs with anti-affinity configurations to different nodes.
Scenario
node affinity:
- Task-topology is important for improving computational efficiency in deep learning computing scenarios. Using the TensorFlow calculation as an example, configure the affinity between “ps” and “worker”. Task-topology algorithm enables “ps” and “worker” to be scheduled to the same node as far as possible, so as to improve the efficiency of network and data interaction between “ps” and “worker”, thus improving the computing efficiency.
- Tasks in HPC and MPI scenarios are highly synchronized and need high-speed network IO.
Anti-affinity:
Take the TensorFlow calculation as an example, the anti-affinity between “ps” and “ps”
Master and slave backup of e-commerce service scene, data disaster tolerant, to ensure that there are spare jobs to continue to provide service after a job fails.
Predicates
Overview
The Predicate Plugin calls the PredicateGPU with pod and nodeInfo as parameters to evaluate and pre-select jobs based on the results.
Scenario
In AI scenarios where GPU resources are required, the Predicate Plugin can quickly filter out those that require the GPU for centralized scheduling.
Nodeorder
Overview
The NodeOrder Plugin is a scheduling optimization strategy that scores nodes from various dimensions through simulated assignments to find the node that is best suited for the current job. The scoring parameters are configured by the user. The parameter contains the Affinity、reqResource、LeastReqResource、MostResource、balanceReqResouce.
Scenario
NodeOrder Plugin provides scoring criteria of multiple dimensions for scheduling, and the combination of different dimensions enables users to flexibly configure appropriate scheduling policies according to their own needs.
SLA
Overview
When users apply jobs to Volcano, they may need adding some particular constraints to job, for example, longest Pending time aiming to prevent job from starving. And these constraints can be regarded as Service Level Agreement (SLA) which are agreed between volcano and user. So sla plugin is provided to receive and realize SLA settings for both individual job and whole cluster.
Scenario
Users can customize SLA related parameters in their own cluster according to business needs. For example, for clusters with high real-time service requirements, JobWaitingTime can be set as small as possible. For clusters with bulk computing jobs, JobWaitingTime can be set to larger. The parameters of a specific SLA and the optimization of the parameters need to be combined with the specific business and related performance measurement results.
TDM
Overview
The full name of TDM is Time Division Multiplexing. In a co-located environment, some nodes are in both Kubernetes cluster and Yarn cluster. For these nodes, Kubernetes and Yarn cluster can use these resource by time-sharing multiplexing.The TDM Plugin marks these nodes as revocable nodes. TDM plugin will try to dispatch preemptable task to revocable node in node revocable time and evict the preemptable task from revocable node out of revocable time.. TDM Plugin improves the time-division multiplexing ability of node resources in the scheduling process of Volcano.
Scenario
In ToB business, cloud vendors provide cloud-based resources for merchants, and different merchants adopt different container arrangement frameworks (Kubernetes/YARN, etc.). TDM Plugin improves the time-sharing efficiency of common node resources and further improves the utilization rate of resources.
Numa-aware
Overview
When the node runs many CPU-bound pods, the workload can move to different CPU cores depending on whether the pod is throttled and which CPU cores are available at scheduling time. Many workloads are not sensitive to this migration and thus work fine without any intervention. However, in workloads where CPU cache affinity and scheduling latency significantly affect workload performance, the kubelet allows alternative CPU management policies to determine some placement preferences on the node.
The CPU Manager and the Topology Manager are all Kubelet components, However There is the following limitation:
- The scheduler is not topology-aware. so it is possible to be scheduled on a node and then fail on the node due to the Topology Manager. this is unacceptable for TensorFlow job. If any worker or ps failed on node, the job will fail.
- The managers are node-level that results in an inability to match the best node for NUMA topology in the whole cluster.
The Numa-Aware Plugin aims to address these limitations.
- Support cpu resource topology scheduling.
- Support pod-level topology policies.
Scenario
Common scenarios for NUMA-Aware are computation-intensive jobs that are sensitive to CPU parameters, scheduling delays. Such as scientific calculation, video decoding, animation rendering, big data offline processing and other specific scenes.