Background
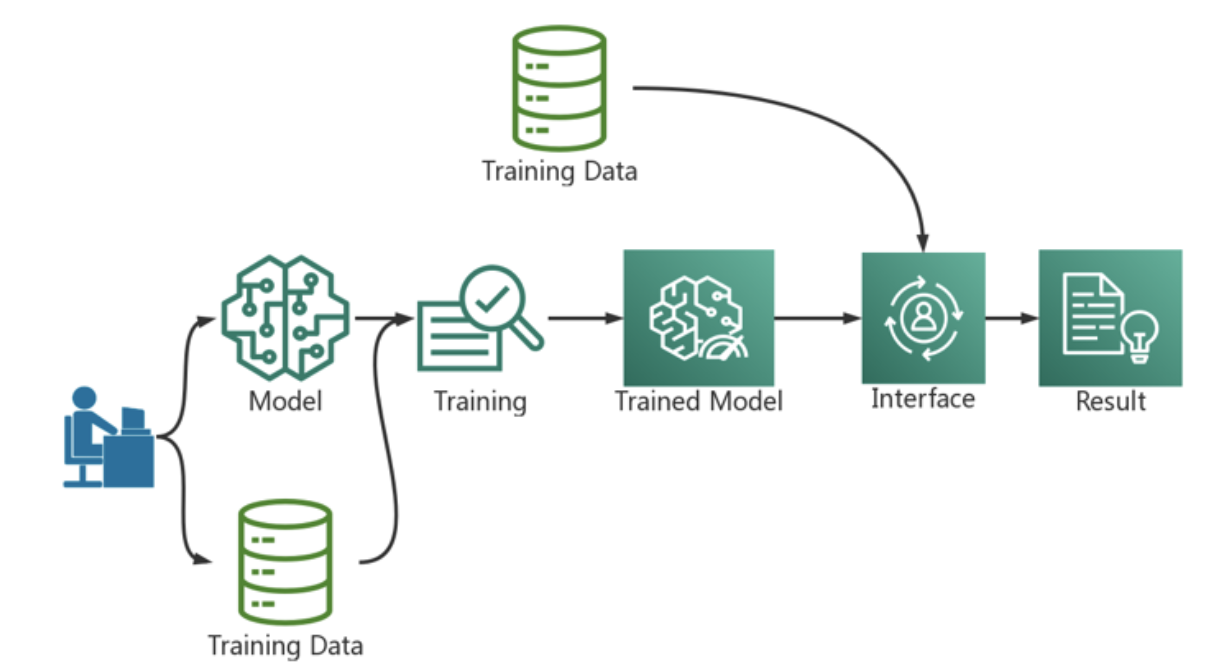
AI development process
Deep learning generally involves four stages: data acquisition and processing, model training and evolution, model deployment, and model evaluation [1]. At the beginning of an enterprise’s involvement in deep learning, due to the lack of relevant experience and resources for deep learning, the team members usually choose to complete the above steps manually step by step in order to quickly meet the immediate needs of the project development period. However, no matter how domain-specific a deep learning expert may have, scaling up a project without the support of an infrastructure platform becomes extremely difficult. Large-scale operations in a production environment require more rapid replication and iterative upgrades than local operations. Production environment has higher requirements for reliability of data, reproducibility of model training, scalability of training model, reliability of automated deployment and operation and maintenance. Therefore, when the enterprise grows to a certain scale, the enterprise will want to build a stable scientific computing platform, so that the upper business personnel can focus on algorithm optimization and business development.
In general, the construction of a deep learning platform will encounter many challenges, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- Data management automation
- The efficient use of resources
- Mask the complexity of the underlying technology
Data management
In a business scenario of deep learning, practitioners spend a significant amount of time capturing and transforming the data needed to build the model. As business scenarios expand, the automation of data transformation becomes a bottleneck in the efficiency of model building. In the process of data processing, new data will be generated, and these data will not only be used for this training, but also for the subsequent reasoning process. And the newly generated data does not need to be passed to the data source, but instead wants to be placed in a new storage space. This requires the underlying platform to provide a scalable storage system. Flexible, extensible and secure data storage system will greatly promote the improvement of data management ability.
The efficient use of resources
Deep learning-related applications are resource-intensive, and the use of resources fluctuates greatly, with peaks and valleys. Fast access to computing resources when the application starts running; At the end of the application, it is very important to recycle the unsuitable computing resources for the improvement of resource utilization. The types and time of computing resources used in data processing, model training and reasoning are different, which requires a flexible resource supply mechanism provided by the computing platform. Deep learning tasks require a large amount of computing resources, so it is impossible to build computing resources for each user separately. The computing platform should be able to guarantee the multi-lease of resource use, allowing multiple users to use the computing resource pool at the same time, rather than being monopolized by a few users.
Shield the underlying technical complexity
AI practitioners focus on model building and product development, ignoring the importance of infrastructure to AI development. Machine Learning/Deep Learning’s own growing technology stack of users includes computing frameworks for machine learning such as TensorFlow, the Spark data processing engine, and underlying drivers such as CUDA. Manually managing these dependencies can consume significant resources and effort on the part of practitioners.
Based on the above goals and challenges, deep learning and other AI computing choose to use containers and Kubernetes to build and manage deep learning platforms. Need to achieve user isolation, queuing mechanism, user rights management, resource management, container ceiling management and many other functions.
Common scenarios
- Priority issues:There are many roles of algorithm engineers in the company, such as interns, full-time employees and senior engineers. They all do the same thing and need GPU resources to do experiments or training. However, when resources are tight, they need to queue according to priority. Even in the same position, there is preemption for urgent assignments (such as paper deadlines, project launches). The priority level of the task needs to be reported by the engineer.
- storage of data:The data sets of deep learning scenarios are very large, so it is necessary to optimize the design at the storage level to meet this requirement. When computing, if one person trains a model, then simple storage is OK. However, if there are 100 people and each person has different training models and data sets, and needs to run multiple tasks, what kind of storage can help you solve this problem? This is a realistic problem facing us. How storage ADAPTS to the ever-expanding computing needs of users is a matter of concern to architects
- Parallel computing problem:A general requirement of deep learning platform based on K8S is to support multi-machine scheduling and make model training as fast as possible through multi-machine parallel training.
- User isolation problem :For larger companies, there are many business departments, which require multi-user management and multi-tenant isolation. (User isolation problem)
- Batch scheduling requirements for pod under deep learning scenarios.
- Resource preemption problem:The upper limit on the amount of scarce resources (GPUs) used and the upper limit on how long they can be used.
- Reservation:The details of the underlying application resources are shielded. It only cares about the total amount of available GPU, not the distribution of GPU.
referrals of the configuration
Priority issues: Customize the priority hierarchy. Focus on the
PriorityClassNameof the job itself. This field represents the priority of the job and is in effect for preemptive scheduling and prioritization.Data storage: Recommends the
block storageservice in extremely performing businesses such as databases. Recommend the use ofobject storageservice in the business scenarios of HPC, big data and AI.High performance computing, model training parallelism :WRF, Kubegene, MPI high performance computing scenarios, multi-machine parallel training.
Job Plugin:
sshprovides secret login, andsvcprovides network information needed for job operation, such as host file, headless service, etc, to provide automatic configuration for calculating cluster parameters.Policies field: Once anypodhas been killed, restart the entire jobrestartJob/compeletedJob. Because of this HPC scenario, Gang-based training job, if a worker fails, it is usually pointless for the entire job to run.This scenario will generally define multiple
tasks, 1 master + multiple workers.
Multi-tenancy, isolation issues :TensorFlow has no concept of tenants. The new resource splitting tool
Queueintroduced by Volcano is configured around Queue in various ways. To ensure the multi-lease of the cluster resources, the surplus of the cluster resources, and the flexibility of the tenants to use the cluster resources. When the cluster resources are redivided, the tenant resource quota can be guaranteed through Reclaim. Configurepreempt, reclaiminVolcano-Scheduler-ConfigMap; configureproportionin plugins.Batch scheduling: The
Gang Pluginmeets the requirements of pod batch scheduling for deep learning scenarios. The class fieldminAvailable, the main indicator of the Gang scheduling algorithm. The plugins field needs to useenvandsvc. The definition of Policies is similar to the high performance computing scenario where apodejection restarts the job.
Reference: