Introduction
Volcano scheduler is the component responsible for pod scheduling. It consists of a series of actions and plugins. Actions define the action that should be executed in every step. Plugins provide the action algorithm details in different scenarios. Volcano scheduler is highly scalable. You can specify and implement actions and plugins based on your requirements.
Workflow
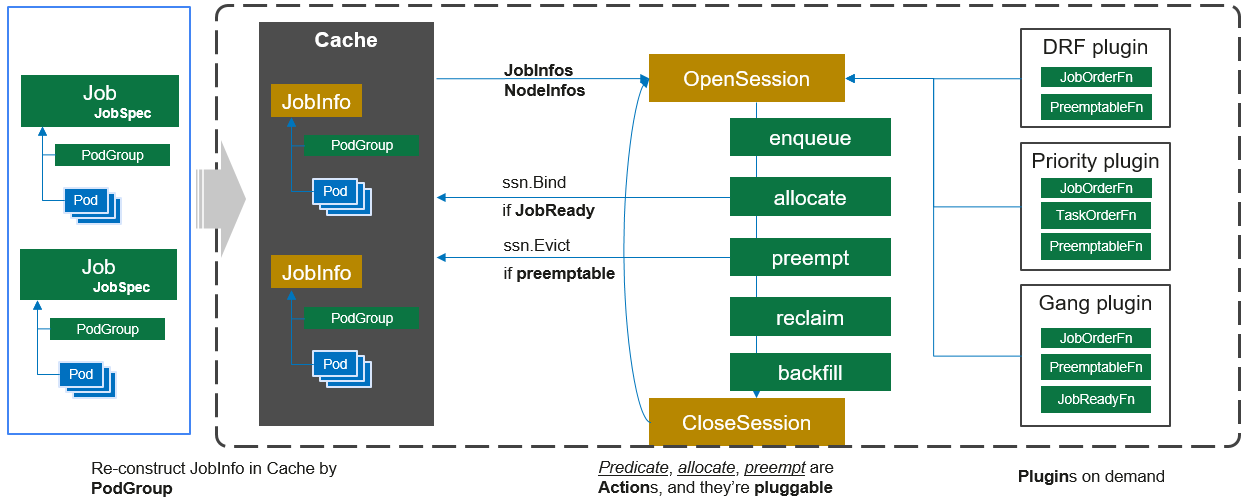
Volcano scheduler workflow
Volcano scheduler works as follows:
- Watches for and caches the jobs submitted by the client.
- Opens a session periodically. A scheduling cycle begins.
- Sends jobs that are not scheduled in the cache to the to-be-scheduled queue in the session.
- Traverses all jobs to be scheduled. Executes enqueue, allocate, preempt, reclaim, and backfill actions in the order they are defined, and finds the most suitable node for each job. Binds the job to the node. The specific algorithm logic executed in the action depends on the implementation of each function in the registered plugins.
- Closes this session.
Actions
enqueue
The enqueue action is responsible for filtering out the tasks that meet the scheduling requirements based on a series of filtering algorithms and sending them to the to-be-scheduled queue. After the action is executed, the status of the task changes from pending to inqueue.
allocate
The allocate action is responsible for selecting the most suitable node based on a series of prediction and optimization algorithms.
preempt
The preempt action is responsible for preemptive scheduling of high priority tasks in the same queue according to priority rules.
reclaim
The reclaim action is responsible for reclaiming the resources allocated to the cluster based on the queue weight when a new task enters the queue and the cluster resources cannot meet the needs of the queue.
backfill
The backfill action is responsible for backfilling the tasks in the pending state into the cluster node to maximize the resource utilization of the node.
Plugins
gang
The gang plugin considers that tasks not in the Ready state (including Binding, Bound, Running, Allocated, Succeed, and Pipelined) have a higher priority. It checks whether the resources allocated to the queue can meet the resources required by the task to run minavailable pods after trying to evict some pods and reclaim resources. If yes, the gang plugin will evict some pods.
conformance
The conformance plugin considers that the tasks in namespace kube-system have a higher priority. These tasks will not be preempted.
DRF
The DRF plugin considers that tasks with fewer resources have a higher priority. It attempts to calculate the total amount of resources allocated to the preemptor and preempted tasks, and triggers the preemption when the preemptor task has less resources.
nodeorder
The nodeorder plugin scores all nodes for a task by using a series of scoring algorithms. The node with the highest score is considered to be the most suitable node for the task.
predicates
The predicates plugin determines whether a task is bound to a node by using a series of evaluation algorithms.
priority
The priority plugin compares the priorities of two jobs or tasks. For two jobs, it decides whose priority is higher by comparing job.spec.priorityClassName. For two tasks, it decides whose priority is higher by comparing task.priorityClassName, task.createTime, and task.id in order.
Configuration
Volcano scheduler is highly scalable because of its composite pattern design. Users can decide which actions and plugins to use according to their needs, and they can also implement customization by calling the action or plugin interfaces. The scheduler configuration is located in the ConfigMap named volcano-scheduler-configmap, which is mounted as a volume into the “/volcano.scheduler” directory in the scheduler container.
How to Get Configuration of Volcano Scheduler
Get the ConfigMap named
volcano-scheduler-configmap.# kubectl get configmap -nvolcano-system NAME DATA AGE volcano-scheduler-configmap 1 6d2hView the details of the data part in the ConfigMap.
# kubectl get configmap volcano-scheduler-configmap -nvolcano-system -oyaml apiVersion: v1 data: volcano-scheduler.conf: | actions: "enqueue, allocate, backfill" tiers: - plugins: - name: priority - name: gang - name: conformance - plugins: - name: drf - name: predicates - name: proportion - name: nodeorder - name: binpack kind: ConfigMap metadata: annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: | {"apiVersion":"v1","data":{"volcano-scheduler.conf":"actions: \"enqueue, allocate, backfill\"\ntiers:\n- plugins:\n - name: priority\n - name: gang\n - name: conformance\n- plugins:\n - name: drf\n - name: predicates\n - name: proportion\n - name: nodeorder\n - name: binpack\n"},"kind":"ConfigMap","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"volcano-scheduler-configmap","namespace":"volcano-system"}} creationTimestamp: "2020-08-15T04:01:02Z" name: volcano-scheduler-configmap namespace: volcano-system resourceVersion: "266" selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/volcano-system/configmaps/volcano-scheduler-configmap uid: 1effe4d6-126c-42d6-a3a4-b811075c30f5
actions and tiers are included in volcano-scheduler.conf. In actions, the comma is used as a separator to configure the actions to be executed by the scheduler. Note that the scheduler will execute the actions in the order that they are configured. Volcano itself will not check the rationality of the order. The list of plugins configured in tiers is the plugins registered with the scheduler. The specific algorithms defined in plugins will be called in actions.