Kubeflow introduction
Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for cloud native application choreography and management, and more and more applications are migrating to Kubernetes. The field of artificial intelligence and machine learning naturally contains a large number of computation-intensive tasks. Developers are very willing to build an AI platform based on Kubernetes and make full use of the resource management, application scheduling, operation and maintenance monitoring capabilities provided by Kubernetes. However, it is a very complicated and tedious process to build an end-to-end AI computing platform based on Kubernetes, which needs to deal with many links. In addition to the model training we are familiar with, it also includes data collection, preprocessing, resource management, feature extraction, data verification, model management, model release, monitoring and other links. For an AI algorithm engineer, if he wants to do model training, he has to build a set of AI computing platform. This process is time-consuming and laborious, and requires a lot of knowledge accumulation[1].
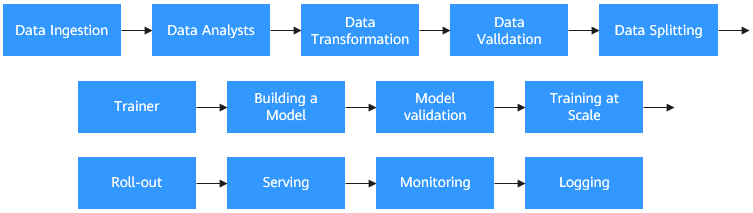
Model training workflow
Kubeflow was born in 2017. The Kubeflow project is built based on containers and Kubernetes, aiming to provide data scientists, machine learning engineers, system operation and maintenance personnel with an agile platform for machine learning business deployment, development, training, release and management. It takes advantage of cloud native technology to make it faster and easier for users to deploy, use and manage the most popular machine learning software.
What scenarios can we use Kubeflow for:
- You want to train the TensorFlow model and you can use the model interface to publish application services in the K8S environment.
- You want to debug your code using Jupyter Notebooks, a multi-user Notebook Server.
- In the training Job, the CPU or GPU resources need to be scheduled and choreographed.
- You want TensorFlow to be combined with other components to publish services.
Kubeflow on Volcano
Volcano is an enhanced high performance computing task batch processing system built on Kubernetes. As a platform for high performance computing scenarios, it makes up for Kubernetes’ lack of basic capabilities in machine learning, deep learning, HPC, and big data computing scenarios, including gang-schedule scheduling capability, computational task queue management, task-topology, and GPU affinity scheduling. In addition, Volcano has enhanced the batch creation and life cycle management of computing tasks, fair-share, binpack scheduling and other aspects on the basis of the native Kubernetes capability. Volcano has fully solved the problem of distributed training in Kubeflow mentioned above.
download kfctl
First of all, you need to download kfctl, you can choose the appropriate compressed package file according to the system [1].
$ tar -xvf kfctl_v1.0.2-0-ga476281_linux.tar.gz
$ sudo mv ./kfctl /usr/local/bin/kfctl
Configure environment variables
$ export PATH= $PATH:"<path-to-kfctl>"
$ export KF_NAME=<your choice of name for the Kubeflow deployment>
$ export BASE_DIR=<path to a base directory>
$ export KF_DIR=${BASE_DIR}/${KF_NAME}
$ export CONFIG_URI="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubeflow/manifests/v1.0-branch/kfdef/kfctl_k8s_istio.v1.0.2.yaml"
Install Kubeflow
$ mkdir -p ${KF_DIR}
$ cd ${KF_DIR}
$ Kfctl apply -V -f ${CONFIG_URI}
Confirm the installation results with the following instructions.
$ kubectl -n kubeflow get all
deploy Mnist
Download the official test set provided by Kubuflow.
git clone https://github.com/kubeflow/examples.git
Start using Notebook
External interface service is provided, where the nodes under the cluster need to be bound to public network IP. If Notebook is not installed, please use pip3 to install it first.
$ pip3 install jupyter notebook
$ jupyter notebook --allow-root
[W 09:08:03.572 NotebookApp] WARNING: The notebook server is listening on all IP addresses and not using encryption. This is not recommended.
[I 09:08:03.575 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /root/examples
[I 09:08:03.575 NotebookApp] Jupyter Notebook 6.3.0 is running at:
[I 09:08:03.575 NotebookApp] http://mytest-87034:30200/
[I 09:08:03.575 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
Access your-IP:30200/,Enter the configuration password to enter the Notebook.
Run the official instance on the Notebook[2]
1.Open Notebook and deploy TFJob。Open the notebook mnist/mnist_vanilla_k8s.ipynb ,Follow the guidelines to deploy a distributed TF Job.
2.Add a schedulerName: add schedulerName: volcano in mnist.yaml,Be sure to use volcano for scheduling.
train_spec = f"""apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1
kind: TFJob
metadata:
name: {train_name}
spec:
schedulerName: volcano
tfReplicaSpecs:
Ps:
replicas: {num_ps}
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
serviceAccount: default-editor
containers:
- name: tensorflow
command:
- python
- /opt/model.py
- --tf-model-dir={model_dir}
- --tf-export-dir={export_path}
- --tf-train-steps={train_steps}
- --tf-batch-size={batch_size}
- --tf-learning-rate={learning_rate}
env:
- name: S3_ENDPOINT
value: {s3_endpoint}
- name: AWS_ENDPOINT_URL
value: {minio_endpoint}
- name: AWS_REGION
value: {minio_region}
- name: BUCKET_NAME
value: {mnist_bucket}
- name: S3_USE_HTTPS
value: "0"
- name: S3_VERIFY_SSL
value: "0"
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: {minio_username}
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: {minio_key}
image: {image}
workingDir: /opt
restartPolicy: OnFailure
Chief:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
serviceAccount: default-editor
containers:
- name: tensorflow
command:
- python
- /opt/model.py
- --tf-model-dir={model_dir}
- --tf-export-dir={export_path}
- --tf-train-steps={train_steps}
- --tf-batch-size={batch_size}
- --tf-learning-rate={learning_rate}
env:
- name: S3_ENDPOINT
value: {s3_endpoint}
- name: AWS_ENDPOINT_URL
value: {minio_endpoint}
- name: AWS_REGION
value: {minio_region}
- name: BUCKET_NAME
value: {mnist_bucket}
- name: S3_USE_HTTPS
value: "0"
- name: S3_VERIFY_SSL
value: "0"
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: {minio_username}
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: {minio_key}
image: {image}
workingDir: /opt
restartPolicy: OnFailure
Worker:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
serviceAccount: default-editor
containers:
- name: tensorflow
command:
- python
- /opt/model.py
- --tf-model-dir={model_dir}
- --tf-export-dir={export_path}
- --tf-train-steps={train_steps}
- --tf-batch-size={batch_size}
- --tf-learning-rate={learning_rate}
env:
- name: S3_ENDPOINT
value: {s3_endpoint}
- name: AWS_ENDPOINT_URL
value: {minio_endpoint}
- name: AWS_REGION
value: {minio_region}
- name: BUCKET_NAME
value: {mnist_bucket}
- name: S3_USE_HTTPS
value: "0"
- name: S3_VERIFY_SSL
value: "0"
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: {minio_username}
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: {minio_key}
image: {image}
workingDir: /opt
restartPolicy: OnFailure
"""
3.submit a job
kubectl apply -f mnist.yaml