On January 9, 2024, UTC+8, Volcano version v1.8.2 was officially released. This version added the following new features:
Support for vGPU scheduling and isolation
Support for vGPU and user-defined resource preemption capabilities
Addition of JobFlow workflow scheduling engine
Node load-aware scheduling and rescheduling support for diverse monitoring systems
Optimization of Volcano’s ability to schedule microservices
Optimization of Volcano charts packages for publishing and archiving

Key Features
Support for vGPU scheduling and isolation
Since ChatGPT became popular, the research and development of AI big models has been endless, and different kinds of AI big models have been launched one after another. Due to its huge training tasks requiring a large amount of arithmetic power, the supply of arithmetic power with GPU as the core has become the key infrastructure for the development of the big model industry. In the actual use scenario, users have low resource utilization and inflexible resource allocation for GPU resources, and must purchase a large number of redundant heterogeneous arithmetic to meet the business needs, while the heterogeneous arithmetic itself is costly, which brings a great burden to the development of enterprises. Starting from version 1.8, Volcano provides a common abstraction framework for shareable devices (GPUs, NPUs, FPGAs…) Volcano provides an abstract general framework for shareable devices (GPU, NPU, FPGA…), based on which developers can customize multiple types of shared devices; currently, Volcano has implemented GPU virtualization features based on this framework, which supports GPU device multiplexing, resource isolation and other capabilities, as follows:
GPU Sharing: Each task can request to use part of the resources of a GPU card, and GPU cards can be shared among multiple tasks.
Device Video Memory Control: GPUs can be allocated according to memory (e.g., 3000M) or proportionally (e.g., 50%) to achieve GPU virtualization resource isolation capability.
For more information about vGPU, please refer to:
How to use the vGPU feature:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/blob/master/docs/user-guide/how_to_use_vgpu.md
How to add new heterogeneous arithmetic sharing strategies:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/blob/master/docs/design/device-sharing.md
Support for vGPU and user-defined resource preemption capabilities
Currently, Volcano supports CPU, Memory and other basic resources preemption, but does not yet support preemption of GPU resources and resources that users develop scheduling plug-ins based on the Volcano framework and manage on their own (e.g., NPU, network resources, etc.). In version 1.8, Volcano restructured the node filtering related processing (PredicateFn callback function), and added the Status type in the return result, which is used to identify whether the current node meets the conditions of job issuance under the scenarios of scheduling, preemption, etc. The GPU preemption function has been released based on the optimized framework, and the user can use the scheduling plug-ins based on the secondary development of Volcano to combine with the business scenarios. The scheduling plug-in can be adapted and upgraded according to the business scenarios. In version 1.8.2, Volcano supports the preemption of the number of node CSIs and the number of node Pods.
For more information on supporting extended resource preemption, please refer to:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/pull/2916
Addition of JobFlow workflow scheduling engine
JobFlow orchestration engine is widely used in high-performance computing, AI biomedical, image processing and beauty, game AGI, scientific computing and other scenarios, to help users simplify the management of multiple tasks in parallel and dependencies, and significantly improve the overall computing efficiency. JobFlow is a lightweight task flow orchestration engine that focuses on Volcano’s job orchestration, providing Volcano with job probes, job completion dependencies, job failure rate tolerance and other diverse job dependency types, and supporting complex process control primitives, with the following specific capabilities:
Supports large-scale job management and complex task flow scheduling.
Supports real-time query to all related jobs and task progress.
Supports automatic operation of jobs and timed startup to release labor costs.
Support for different tasks can set up a variety of action strategies, when the task meets specific conditions can trigger the corresponding action, such as timeout retry, node failure drift, etc.
A demonstration of a JobFlow task running is shown below:
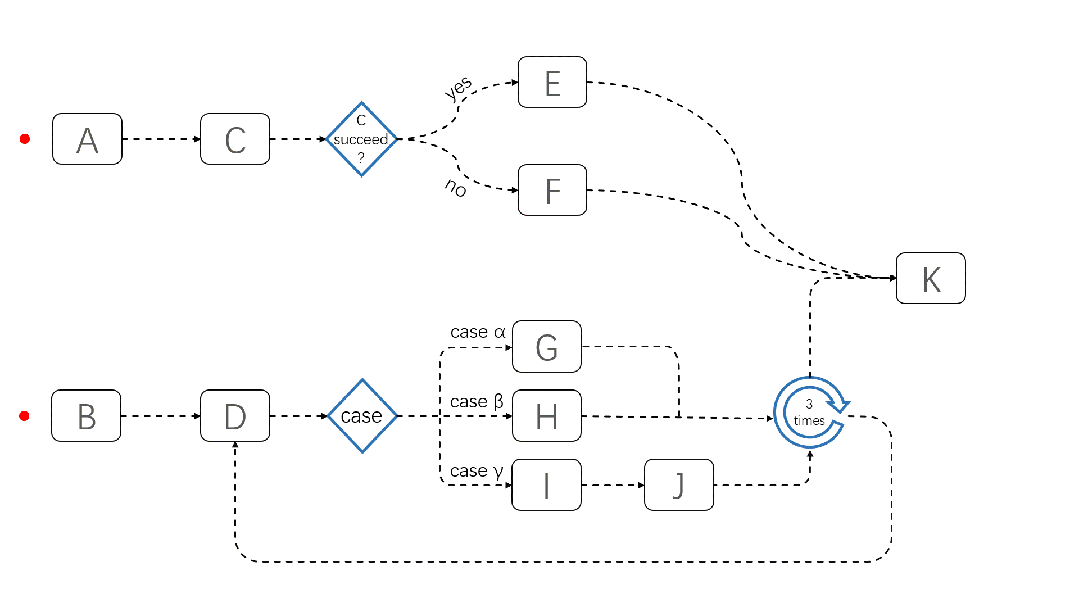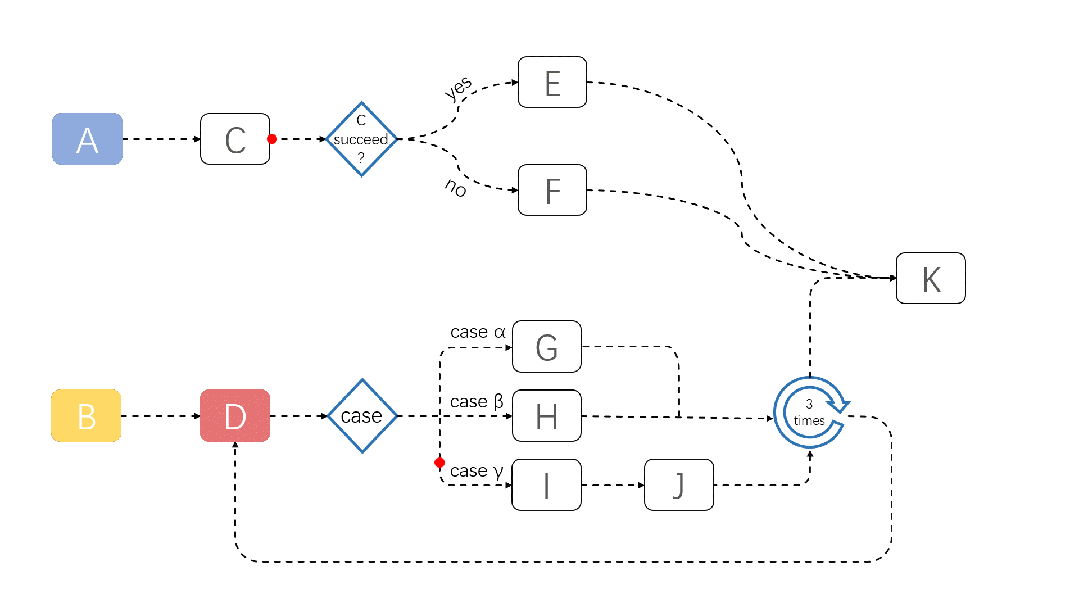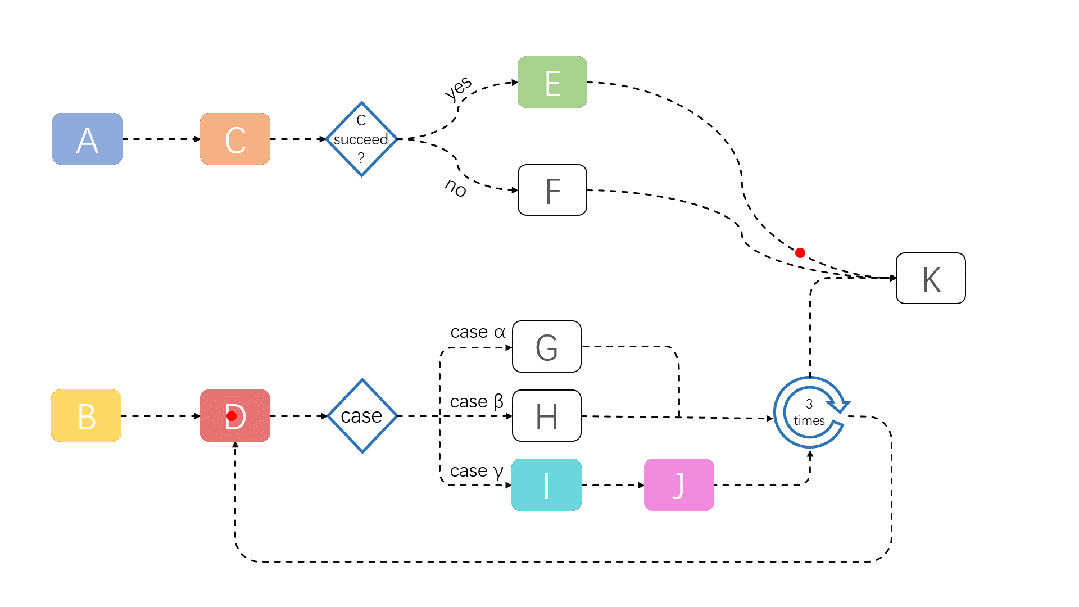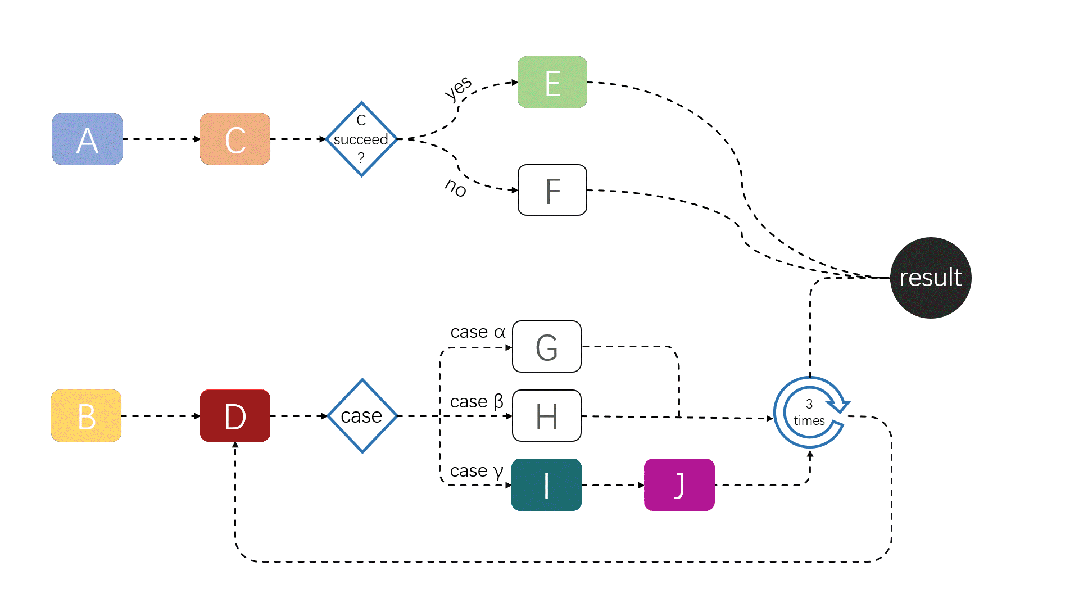
For more information about JobFlow, please refer to:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/blob/master/docs/design/jobflow/README.md
Node load-aware scheduling and rescheduling support for diverse monitoring systems
The state of a Kubernetes cluster changes in real time as tasks are created and finished. In some scenarios (e.g., adding or removing nodes, changing the affinity of Pods and Nodes, dynamic changes in the job lifecycle, etc.), there are problems such as unbalanced resource utilization among cluster nodes and node performance bottlenecks, etc. At this time, scheduling and re-scheduling based on the real load can help us solve the above problems. Before version 1.8 of Volcano, the real load scheduling and rescheduling metrics acquisition only supports Prometheus, from version 1.8 onwards, Volcano optimizes the monitoring metrics acquisition framework, adds support for ElasticSearch monitoring system, and supports smooth docking of more types of monitoring systems with less adaptation workload.
For more information on supporting multiple monitoring systems, please refer to:
Node load-aware based scheduling:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/blob/master/docs/design/usage-based-scheduling.md
Re-scheduling:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/blob/master/docs/design/rescheduling.md
Optimization of Volcano’s ability to schedule microservices
Add Kubernetes default scheduler plugin switch
Volcano is a unified converged scheduling system that not only supports AI, BigData and other computation jobs, but also supports microservice workloads, and is compatible with PodTopologySpread, VolumeZone, VolumeLimits, NodeAffinity, and other scheduling plug-ins that are part of the Kubernetes default scheduler, PodAffinity, NodeAffinity, PodAffinity, and other scheduling plugins, and the default scheduling plugin capabilities of Kubernetes are enabled by default in Volcano. Since Volcano 1.8, Kubernetes default scheduling plug-ins can be turned on and off freely by means of configuration files, and all of them are turned on by default. If you choose to turn off some of the plug-ins, for example, turn off the PodTopologySpread and VolumeZone plug-ins, you can set the corresponding value in the predicate plug-in to If you want to disable some plug-ins, such as PodTopologySpread and VolumeZone plug-ins, you can set the corresponding value in the predicate plug-in to false:
actions: "allocate, backfill, preempt"
tiers:
- plugins:
- name: priority
- name: gang
- name: conformance
- plugins:
- name: drf
- name: predicates
arguments:
predicate.VolumeZoneEnable: false
predicate.PodTopologySpreadEnable: false
- name: proportion
- name: nodeorder
For more information, please refer to:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/issues/2748
Enhanced Cluster Autoscaling Compatibility
In the Kubernetes platform, Volcano is increasingly used as a scheduler for general-purpose services, in addition to batch computing services.Node Autoscaler is one of the core features of Kubernetes, and it plays an important role in facing the surge in user traffic and saving operational costs. Volcano optimizes job scheduling and other related logic to enhance compatibility and interaction with ClusterAutoscaler, mainly in the following two areas: Timely triggering of capacity expansion for pods entering pipeline state during scheduling phase Candidate nodes are scored in gradients to reduce the impact of cluster terminating pods on the scheduling load, avoiding pods entering invalid pipeline states, which can lead to mis-expansion of the cluster.
For more information, please refer to:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/issues/3000 https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/issues/2782
Fine-grained management of Node resources for increased resilience
When a node’s total resources are less than the allocated resources due to some reasons such as device-plugin reporting anomalies, Volcano considers that the node’s data is inconsistent, isolates the node, and stops scheduling any new workloads to the node. In version 1.8, node resource management is refined, for example: when the total GPU resource capacity of a node is less than the amount of allocated resources, pods applying for GPU resources are prohibited from scheduling to that node, while jobs applying for non-GPU resources will still be allowed to schedule to that node normally.
For more information, please refer to:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/issues/2999
Optimization of Volcano charts packages for publishing and archiving
As Volcano is used in more and more production and cloud environments, it is important to have a clean and standardized installation process. Starting from version 1.8, Volcano optimizes the charts package release archive action, standardizes the installation and usage process, and completes the migration of historical versions (v1.6, v1.7) to the new helm repository in the following ways:
Add Volcano charts bin address
helm repo add volcano-sh https://volcano-sh.github.io/helm-chartsSearch for all installable versions of Volcano
helm search repo volcano -lInstall the latest version of Volcano
helm install volcano volcano-sh/volcano -n volcano-system --create-namespaceInstall the specified version of Volcano, e.g. 1.8.2.
helm install volcano volcano-sh/volcano -n volcano-system --create-namespace --version 1.8.2
For more information on the Volcano charts package, please refer to:
https://github.com/volcano-sh/helm-charts
Contributors
Volcano 1.8.2 is brought into being from hundreds of code commits from 33 contributors. Thanks for your contributions.
Contributors on GitHub:
| @shaobo76 | @william-wang | @gengwg |
| @kingeasternsun | @Aakcht | @waiterQ |
| @Shoothzj | @hwdef | @halegreen |
| @wulixuan | @Monokaix | @medicharlachiranjeevi |
| @WulixuanS | @rayoluo | @lowang-bh |
| @gj199575 | @noyoshi | @Tongruizhe |
| @jinzhejz | @Cdayz | @Mufengzhe |
| @renwenlong-github | @wangyang0616 | @jiamin13579 |
| @zbbkeepgoing | @jiangkaihua | @z2Zhang |
| @archlitchi | @lixin963 | @xiao-jay |
| @Yanping-io | @Lily922 | @shusley244 |
Reference
Release note: v1.8.0
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/releases/tag/v1.8.0
Release note: v1.8.1
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/releases/tag/v1.8.1
Release note: v1.8.2
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/releases/tag/v1.8.2
Branch:release-1.8
https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano/tree/release-1.8
About Volcano
Volcano is designed for high-performance computing applications such as AI, big data, gene sequencing, and rendering, and supports mainstream general computing frameworks. More than 58,000 global developers joined us, among whom the in-house ones come from companies such as Huawei, AWS, Baidu, Tencent, JD, and Xiaohongshu. There are 3.5k+ Stars and 800+ Forks for the project. Volcano has been proven feasible for mass data computing and analytics, such as AI, big data, and gene sequencing. Supported frameworks include Spark, Flink, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Argo, MindSpore, Paddlepaddle, Kubeflow, MPI, Horovod, MXNet, KubeGene, and Ray. The ecosystem is thriving with more developers and use cases coming up.
