Important Note
Note GPU Number is deprecated in volcano v1.9, recommended to use the Volcano VGPU feature, which is provided by HAMI project, click here
Environment setup
Install volcano
1. Install from source
Refer to Install Guide to install volcano.
After installed, update the scheduler configuration:
kubectl edit cm -n volcano-system volcano-scheduler-configmap
For volcano v1.8.2+(v1.8.2 excluded), use the following configMap
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: volcano-scheduler-configmap
namespace: volcano-system
data:
volcano-scheduler.conf: |
actions: "enqueue, allocate, backfill"
tiers:
- plugins:
- name: priority
- name: gang
- name: conformance
- plugins:
- name: drf
- name: deviceshare
arguments:
deviceshare.GPUNumberEnable: true # enable gpu number
- name: predicates
- name: proportion
- name: nodeorder
- name: binpack
For volcano v1.8.2-(v1.8.2 included), use the following configMap
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: volcano-scheduler-configmap
namespace: volcano-system
data:
volcano-scheduler.conf: |
actions: "enqueue, allocate, backfill"
tiers:
- plugins:
- name: priority
- name: gang
- name: conformance
- plugins:
- name: drf
- name: predicates
arguments:
predicate.GPUNumberEnable: true # enable gpu number
- name: proportion
- name: nodeorder
- name: binpack
2. Install from release package.
Same as above, after installed, update the scheduler configuration in volcano-scheduler-configmap configmap.
Install Volcano device plugin
Please refer to volcano device plugin
- Remember to config volcano device plugin to support gpu-number, users need to config volcano device plugin –gpu-strategy=number. For more information volcano device plugin configuration
Verify environment is ready
Check the node status, it is ok volcano.sh/gpu-number is included in the allocatable resources.
$ kubectl get node {node name} -oyaml
...
Capacity:
attachable-volumes-gce-pd: 127
cpu: 2
ephemeral-storage: 98868448Ki
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 7632596Ki
pods: 110
volcano.sh/gpu-memory: 0
volcano.sh/gpu-number: 1
Allocatable:
attachable-volumes-gce-pd: 127
cpu: 1930m
ephemeral-storage: 47093746742
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 5752532Ki
pods: 110
volcano.sh/gpu-memory: 0
volcano.sh/gpu-number: 1
Running Jobs With Multiple GPU Cards
Jobs can have multiple exclusive NVIDIA GPUs cards via defining container level resource requirements volcano.sh/gpu-number:
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: gpu-pod1
spec:
containers:
- name: cuda-container
image: nvidia/cuda:9.0-devel
command: ["sleep"]
args: ["100000"]
resources:
limits:
volcano.sh/gpu-number: 1 # requesting 1 gpu cards
EOF
If the above pods claim multiple gpu cards, you can see each of them has exclusive gpu cards:
$ kubectl exec -ti gpu-pod1 env
...
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
VOLCANO_GPU_ALLOCATED=1
...
Understanding How Multiple GPU Cards Requirement Works
The main architecture is similar as the previous, but the gpu-index results of each pod will be a list of gpu cards index.
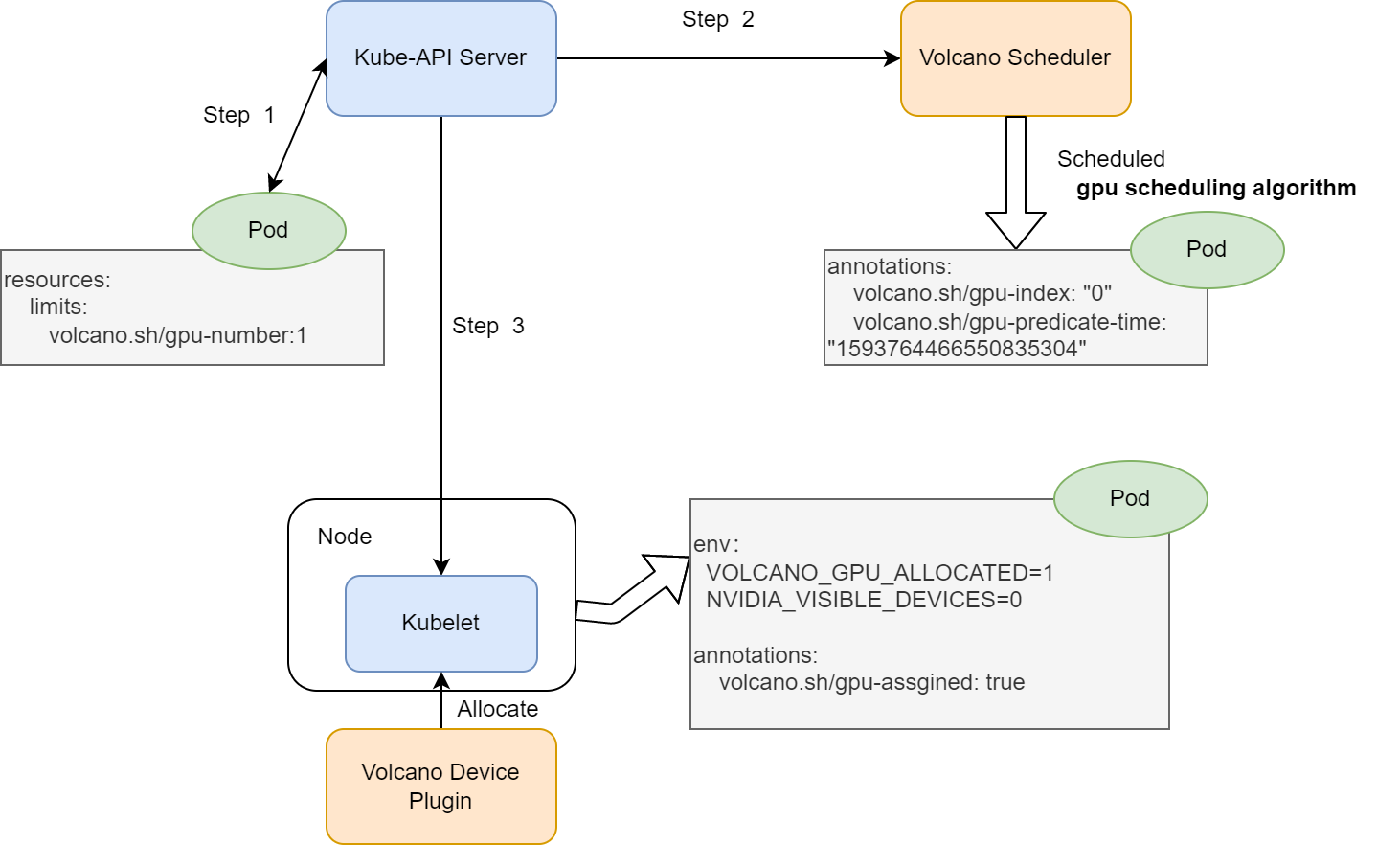
create a pod with
volcano.sh/gpu-numberresource request,volcano scheduler predicates and allocate gpu cards to the pod. Add the below annotation
annotations: volcano.sh/gpu-index: "0" volcano.sh/predicate-time: "159376446655083530"kubelet watches the pod bound to itself, and calls allocate API to set env before running the container.
env: NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0" # GPU card index VOLCANO_GPU_ALLOCATED: "1" # GPU number allocated